Blank Wv Pas PDF Template
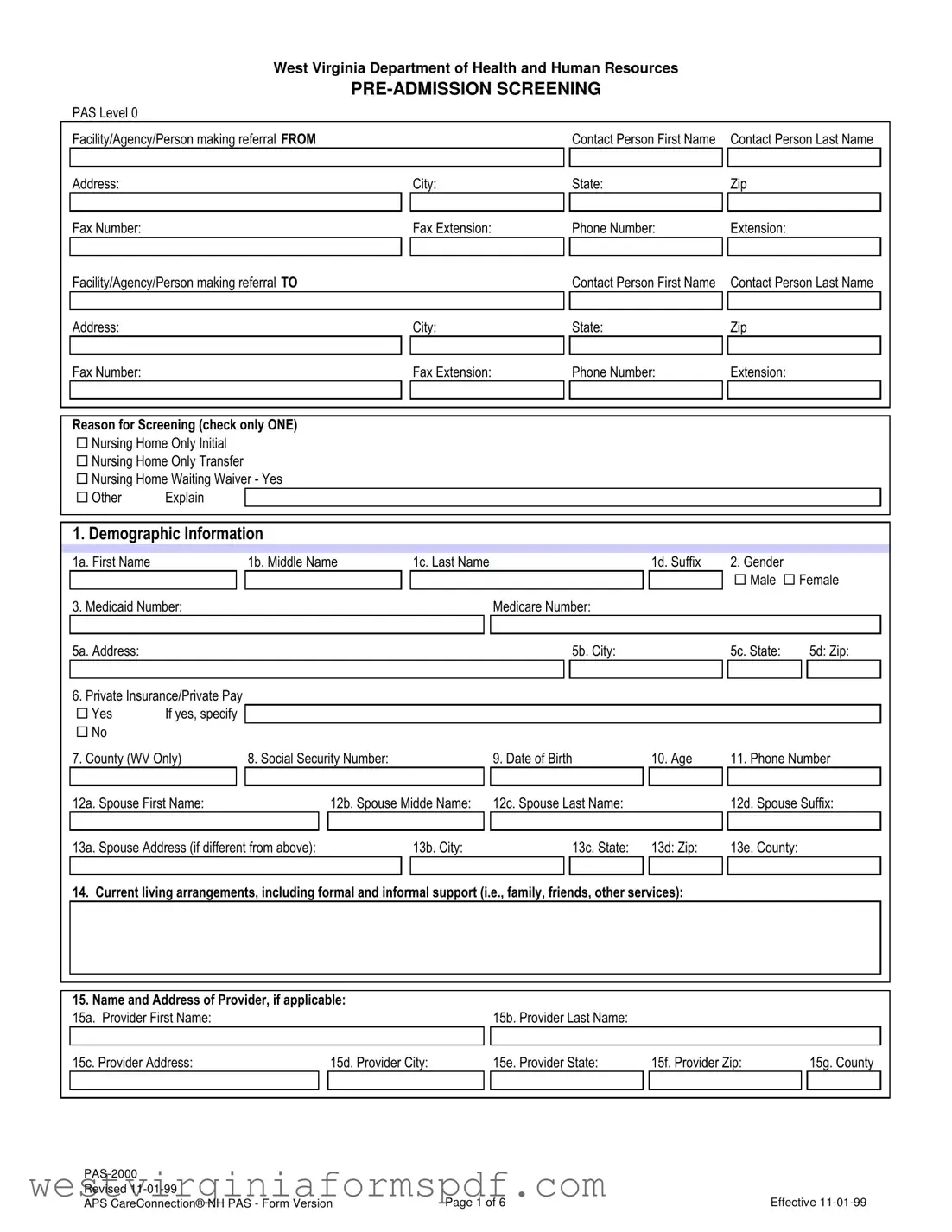
The West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening (PAS) form plays a crucial role in the healthcare process for individuals seeking long-term care services. This form is designed to evaluate the needs of applicants before they are admitted to nursing facilities or similar care settings. It gathers essential information about the individual’s medical history, current health status, and any specific care requirements they may have. By completing the PAS form, healthcare providers can ensure that each person receives the appropriate level of care tailored to their unique situation. The form also helps in determining eligibility for various programs and services, making it a vital tool for both applicants and providers. Understanding the components of the PAS form can streamline the admission process and enhance the quality of care received by individuals in need.
Browse More Forms
Wv Pte-100 Instructions 2022 - Submitting this form is a proactive step nonresidents can take to manage their tax responsibilities effectively.
A Last Will and Testament form is a legal document that outlines how a person's assets and responsibilities should be handled after their death. It allows individuals to specify beneficiaries for their property and appoint guardians for minor children. For more information on creating a valid will, you can visit TopTemplates.info. Understanding this essential document can provide peace of mind and ensure that one's final wishes are respected.
West Virginia State Tax Department - Documentation supporting exempt purchases may be required later.
Form Attributes
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Governing Law | The West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening (PAS) form is governed by state regulations found in the West Virginia Code §16-5D-1 et seq. |
| Purpose | The PAS form is designed to assess the eligibility of individuals for nursing home placement and ensure they meet necessary criteria. |
| Effective Date | This specific version of the PAS form became effective on November 1, 1999. |
| Revisions | The form has undergone revisions, with the last noted update being in 1999, indicating ongoing efforts to maintain compliance and relevance. |
| Submission | The completed PAS form must be submitted to the appropriate state agency for review prior to admission into a nursing facility. |
| Required Information | Key information required on the form includes personal details, medical history, and assessment of functional capabilities. |
| Confidentiality | All information provided on the PAS form is subject to confidentiality protections under state and federal law. |
| Accessibility | The PAS form is available through the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources, ensuring accessibility for individuals and caregivers. |
Similar forms
The West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening (PAS) form is similar to the Medicaid Application form. Both documents serve the purpose of evaluating an individual's eligibility for long-term care services. The Medicaid Application collects information about an applicant's financial status, medical history, and living situation. This helps determine whether the individual meets the income and asset criteria required for Medicaid benefits, similar to how the PAS assesses the need for long-term care services based on health and functional status.
The temporary Power of Attorney for a Child arrangement is essential for parents needing someone to manage their child's welfare in their absence, providing them peace of mind during critical moments.
Another document comparable to the PAS is the Long-Term Care Assessment form. This form is utilized by healthcare providers to evaluate an individual's needs for long-term care. It gathers information about the person's physical and mental health, daily functioning, and support systems. Like the PAS, this assessment aims to identify the appropriate level of care required, ensuring that individuals receive the services tailored to their needs.
The Comprehensive Needs Assessment is also similar to the PAS. This document is often used in various healthcare settings to evaluate the overall needs of a patient. It includes a detailed review of medical history, social circumstances, and personal preferences. Both the Comprehensive Needs Assessment and the PAS are designed to create a holistic understanding of an individual's requirements, facilitating appropriate care planning and resource allocation.
Additionally, the Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS) Assessment form shares similarities with the PAS. This document is specifically focused on determining an individual's eligibility for community-based services rather than institutional care. Both forms assess an individual’s functional limitations and support needs, allowing for the identification of suitable care options that promote independence and quality of life.
The Uniform Assessment Instrument (UAI) is another document that aligns with the objectives of the PAS. The UAI is used to assess individuals seeking long-term care services across various states. It collects comprehensive information about health status, functional abilities, and support needs. Like the PAS, the UAI aims to standardize the assessment process, ensuring consistency in determining eligibility for care services.
Lastly, the Patient Assessment Instrument (PAI) is akin to the PAS in its purpose of evaluating individuals for care services. The PAI is often used in skilled nursing facilities to assess a resident's needs upon admission. It focuses on health status, functional capabilities, and psychosocial factors. Both the PAI and the PAS aim to inform care planning and ensure that individuals receive the appropriate level of support based on their unique circumstances.
FAQ
What is the Wv PAS form?
The Wv PAS form, or West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening form, is a document used by the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources. It is designed to assess an individual's needs before they are admitted to a healthcare facility, such as a nursing home. This screening helps ensure that the individual receives the appropriate level of care based on their specific requirements.
Who needs to fill out the Wv PAS form?
The Wv PAS form must be completed for individuals who are seeking admission to a nursing facility in West Virginia. This includes seniors and individuals with disabilities who may require long-term care services. The form is essential for determining eligibility for Medicaid and other assistance programs.
How do I obtain the Wv PAS form?
The Wv PAS form can be obtained directly from the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources website or by visiting a local DHHR office. Additionally, healthcare providers and facilities may also have copies of the form available for patients and families.
What information is required on the Wv PAS form?
The Wv PAS form requires detailed information about the individual’s medical history, current health status, and any specific needs they may have. This includes:
- Personal identification details
- Medical diagnoses and conditions
- Current medications and treatments
- Functional abilities and limitations
- Social and family support systems
Providing accurate and comprehensive information is crucial for effective assessment.
How long does it take to process the Wv PAS form?
The processing time for the Wv PAS form can vary depending on several factors, including the volume of applications being processed and the completeness of the submitted information. Typically, it may take several days to a few weeks for the assessment to be completed. It is advisable to submit the form as early as possible to avoid delays in admission.
What happens after the Wv PAS form is submitted?
Once the Wv PAS form is submitted, a qualified assessor will review the information provided. This may include conducting an in-person evaluation of the individual. After the assessment, the individual will receive a determination regarding their eligibility for admission to a nursing facility and any necessary care services.
Can I appeal a decision made based on the Wv PAS form?
Yes, if you disagree with the decision made after the Wv PAS assessment, you have the right to appeal. The appeal process typically involves submitting a written request for reconsideration to the appropriate department. It is important to follow the specific guidelines provided in the decision letter to ensure your appeal is considered.
Documents used along the form
The West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening (WV PAS) form is an essential document used to assess an individual's eligibility for nursing facility services. Alongside this form, several other documents play a crucial role in the application and evaluation process. Below are four commonly used forms that complement the WV PAS.
- Patient Medical History Form: This document provides a comprehensive overview of the patient's medical background, including past illnesses, surgeries, and ongoing treatments. It is vital for healthcare providers to understand the patient's health status before making any decisions regarding care.
- Consent for Release of Information: This form allows healthcare providers to share the patient's medical information with relevant parties, such as family members or other healthcare professionals. It ensures that the patient's privacy is respected while facilitating necessary communication.
- Homeschool Letter of Intent: This essential document allows parents or guardians in Arizona to formally announce their intent to homeschool their child, ensuring compliance with state regulations. For more information on this process, visit arizonapdf.com/homeschool-letter-of-intent.
- Financial Eligibility Application: This document assesses the financial status of the individual seeking nursing facility services. It collects information about income, assets, and expenses to determine if the patient qualifies for financial assistance or Medicaid coverage.
- Care Plan Assessment: This form outlines the specific care needs and preferences of the patient. It is developed by healthcare professionals in collaboration with the patient and their family, ensuring that the care provided is tailored to the individual’s requirements.
Understanding these additional forms is crucial for anyone navigating the pre-admission process for nursing facilities in West Virginia. Each document serves a specific purpose and contributes to a comprehensive evaluation of the individual's needs and circumstances.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the West Virginia Pre-Admission Screening (WV PAS) form, it's important to approach the task thoughtfully. Here are some guidelines to help ensure the process goes smoothly.
- Do read the instructions carefully before starting. Understanding what is required can save time and prevent mistakes.
- Do provide accurate and complete information. This helps the reviewing agency make informed decisions about eligibility.
- Do double-check your entries. Simple errors can lead to delays in processing your application.
- Do keep a copy of the completed form for your records. This can be useful for future reference or if any questions arise.
- Don't leave any sections blank. If a question does not apply, indicate that clearly instead of skipping it.
- Don't rush through the form. Take your time to ensure all information is accurate and complete.
- Don't hesitate to ask for help if you're unsure about any part of the form. Assistance is often available from local agencies or support groups.
By following these guidelines, individuals can navigate the WV PAS form with greater confidence and clarity. Taking the time to complete the form correctly can lead to a more efficient review process and better outcomes.